Foot Drop Recovery at Home: Exercises & Protocol
Foot drop can turn every step into a stumble. This common mobility issue affects thousands of Americans after nerve injuries, strokes, or neurological conditions. The good news?
Foot drop exercises at home, combined with the right tools, can restore strength and confidence without constant clinic visits.
What Is Foot Drop?
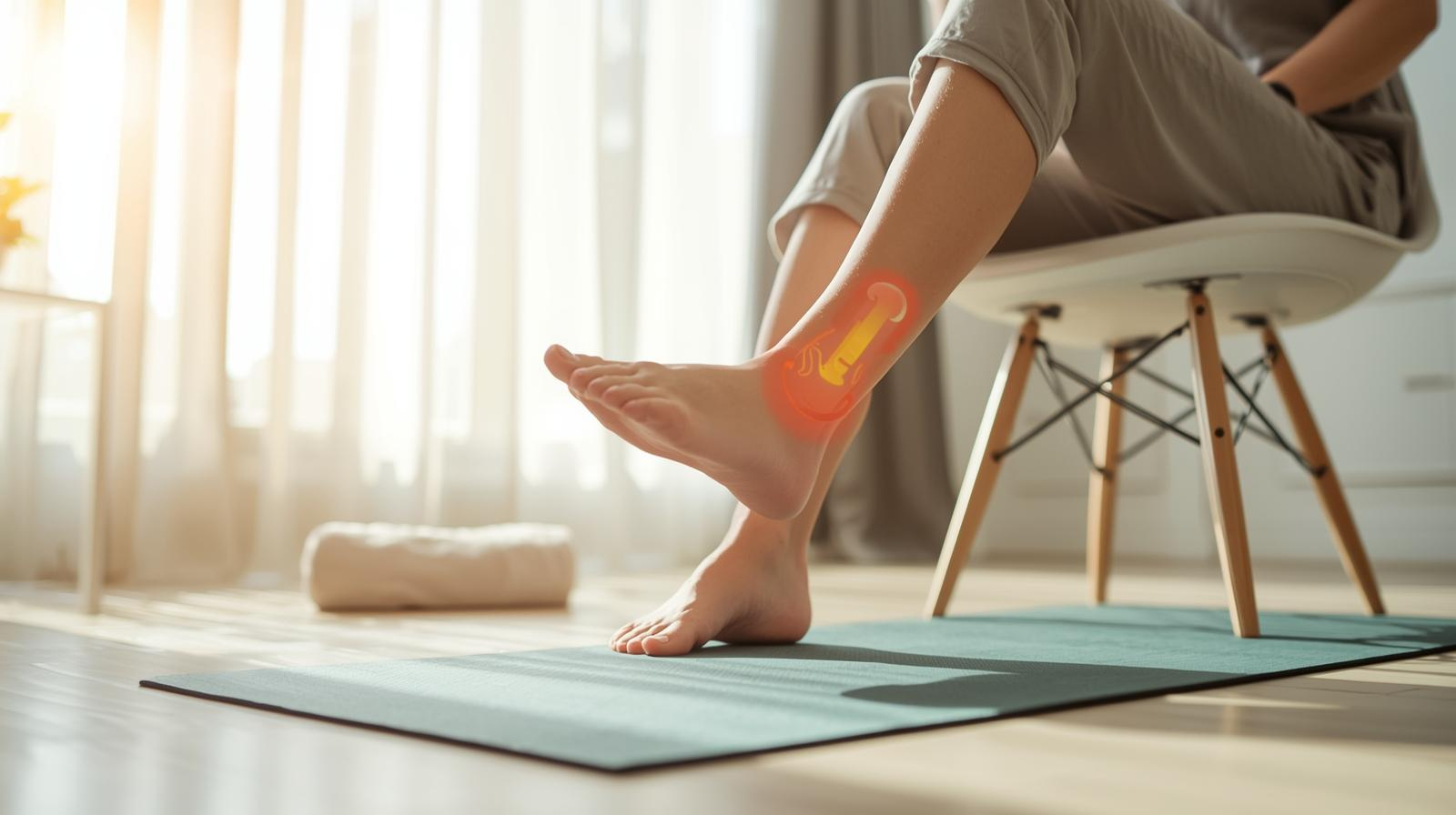
Foot drop describes the inability to lift the front part of the foot during walking. The tibialis anterior—the muscle primarily responsible for preventing foot drop fails to contract properly. This causes toes to drag or forces a high-stepping gait.
The condition usually stems from damage to the
common peroneal nerve, which wraps around the knee and powers ankle movement. When
which nerve causes foot drop becomes compromised, daily activities like climbing stairs or walking on uneven ground become risky.
Who Develops Foot Drop and Why It Matters
Foot drop affects:
- Stroke survivors (up to 20% experience persistent weakness)
- Multiple sclerosis patients
- People with peroneal nerve injuries from trauma or compression
- Diabetes patients with peripheral neuropathy
- Post-surgical cases after knee or hip procedures
Left untreated, it increases
fall risk by 200% and erodes independence. Early
foot drop treatment physical therapy prevents muscle atrophy and retrains neural pathways.
Rehabilitation Options for Foot Drop
Traditional approaches include:
- Ankle-foot orthoses (AFOs) – Rigid braces that hold the foot up
- Functional electrical stimulation (FES) – Uses shocks to activate muscles
- Physical therapy – Focuses on strengthening and coordination
While effective, these options often require clinic visits or bulky equipment. Modern solutions now enable
foot drop exercise protocol implementation at home with minimal setup.
The Best Foot Drop Exercise Machine for Home Use
Not all rehabilitation devices work the same way. The Just Walk™ offers a thoughtful approach to foot drop recovery by combining simplicity with effective training features:
- Provides gentle mechanical lift during the swing phase
- Includes four resistance settings to gradually strengthen the tibialis anterior
- Compact, lightweight design (just 3 lbs) with no need for batteries or complex setup
- Supports both seated and standing exercises for different stages of rehabilitation
Unlike traditional braces that simply hold the foot in place,
Just Walk™ actively retrains coordination between the brain and leg muscles. Backed by clinical case studies in post-stroke rehabilitation, the device has been shown to
enhance gait symmetry and step control within 4–6 weeks of short, consistent daily practice — a meaningful advance for people recovering from foot drop.
Product Differentiation: Just Walk vs. Traditional Options
| Feature | Just Walk™ | AFO Brace | FES Device |
|---|---|---|---|
| Active muscle strengthening | Yes | No | Partial |
| Home independence | Yes | Yes | Clinic-dependent |
| Neuroplasticity training | Yes | No | Limited |
30-Day Foot Drop Exercise Protocol
Week 1–2: Wear Just Walk at lowest resistance for 15-minute walks twice daily. Focus on smooth heel-to-toe motion.
Week 3–4: Increase to resistance level 2. Add 10 step-ups and 20 towel scrunches daily.
Track your progress:
with consistent practice, improvements often become noticeable within a few weeks.
Summary
Foot drop doesn’t have to mean permanent braces or limited mobility. Combining targeted foot drop exercises, understanding what muscle is primarily responsible for preventing foot drop, and using the right foot drop exercise machine creates lasting recovery.
Start your 30-day protocol today. Consult your physical therapist to customize resistance levels for your specific nerve damage.
Related Topics
FAQs
?What muscle is primarily responsible for preventing foot drop
The tibialis anterior muscle lifts the foot during walking. Just Walk™ targets this muscle with progressive resistance.
?Which nerve causes foot drop
The common peroneal nerve (also called fibular nerve) is most commonly affected. Damage here disrupts signals to the ankle dorsiflexors.
?Can I do foot drop exercises at home without equipment
Yes, but progress is slower. The best foot drop exercise machine like Just Walk accelerates recovery through active assistance and resistance.
?What’s the difference between foot drop and flat feet
Foot drop is a neuromuscular issue (inability to lift the foot). Flat feet involve arch collapse and may contribute to peroneal strain but don’t directly cause toe drag. Just Walk helps both by improving ankle control.
?Are there any foot drop exercises to avoid
Skip high-impact moves like jumping or running until cleared. Focus on controlled, low-resistance foot drop treatment physical therapy movements to prevent strain on the common peroneal nerve.
References
- American Physical Therapy Association. (2024). Foot Drop Management Guidelines.
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. (2025). Peroneal Nerve Injury Fact Sheet.
- Chaban Medical Clinical White Paper: Neuromotor Retraining
- Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation. (2023).
Home-Based Gait Retraining in Peripheral Nerve Injury.
Important
This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice; always consult your doctor or physical therapist before starting any exercise or using any device.